Overview
Scroll views are an essential component in SwiftUI that allow users to view content that is larger than the visible area of the screen. This article explores how to use ScrollView in SwiftUI, customize its behavior, and integrate it with other SwiftUI views to create a seamless user experience.
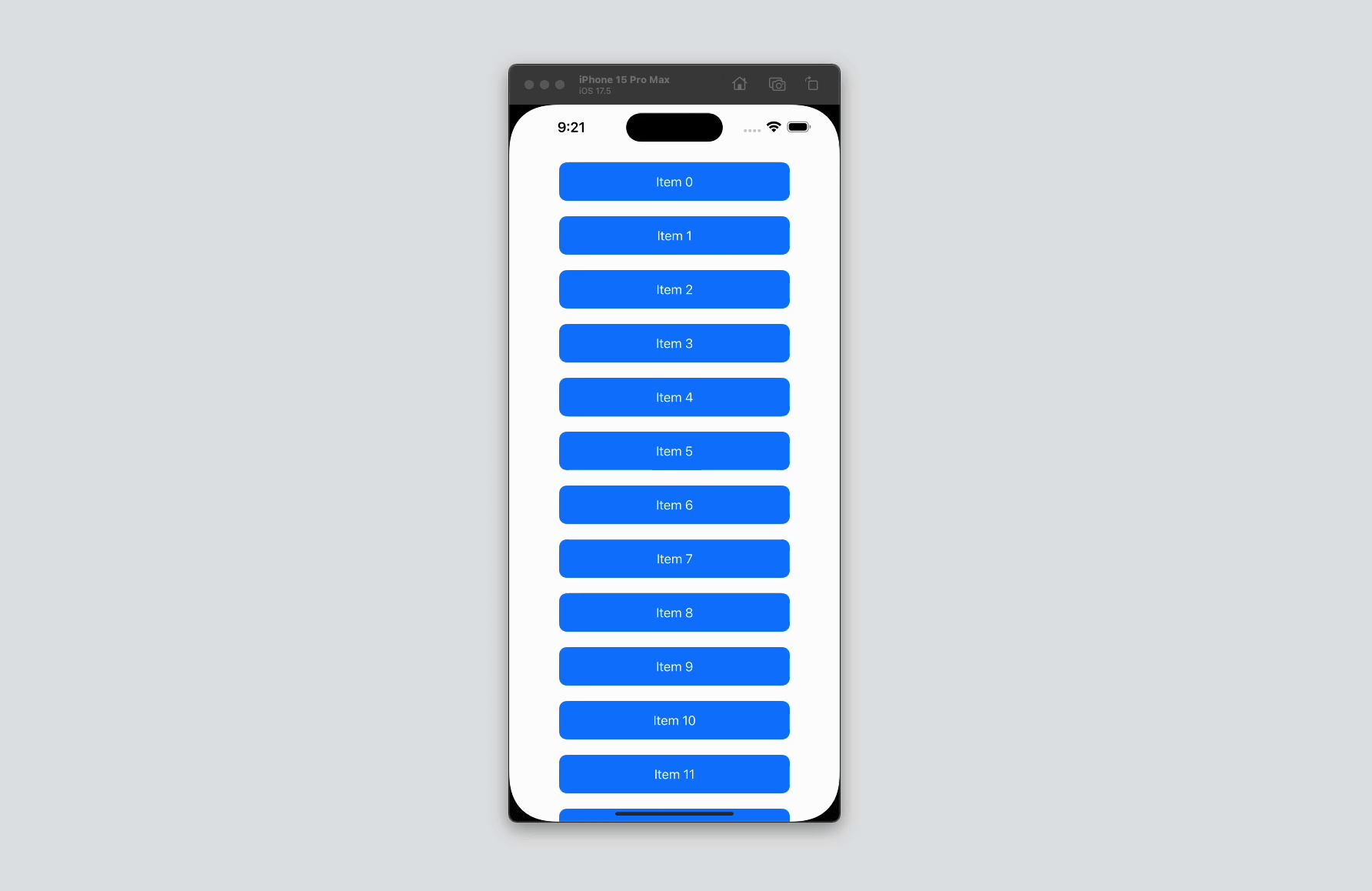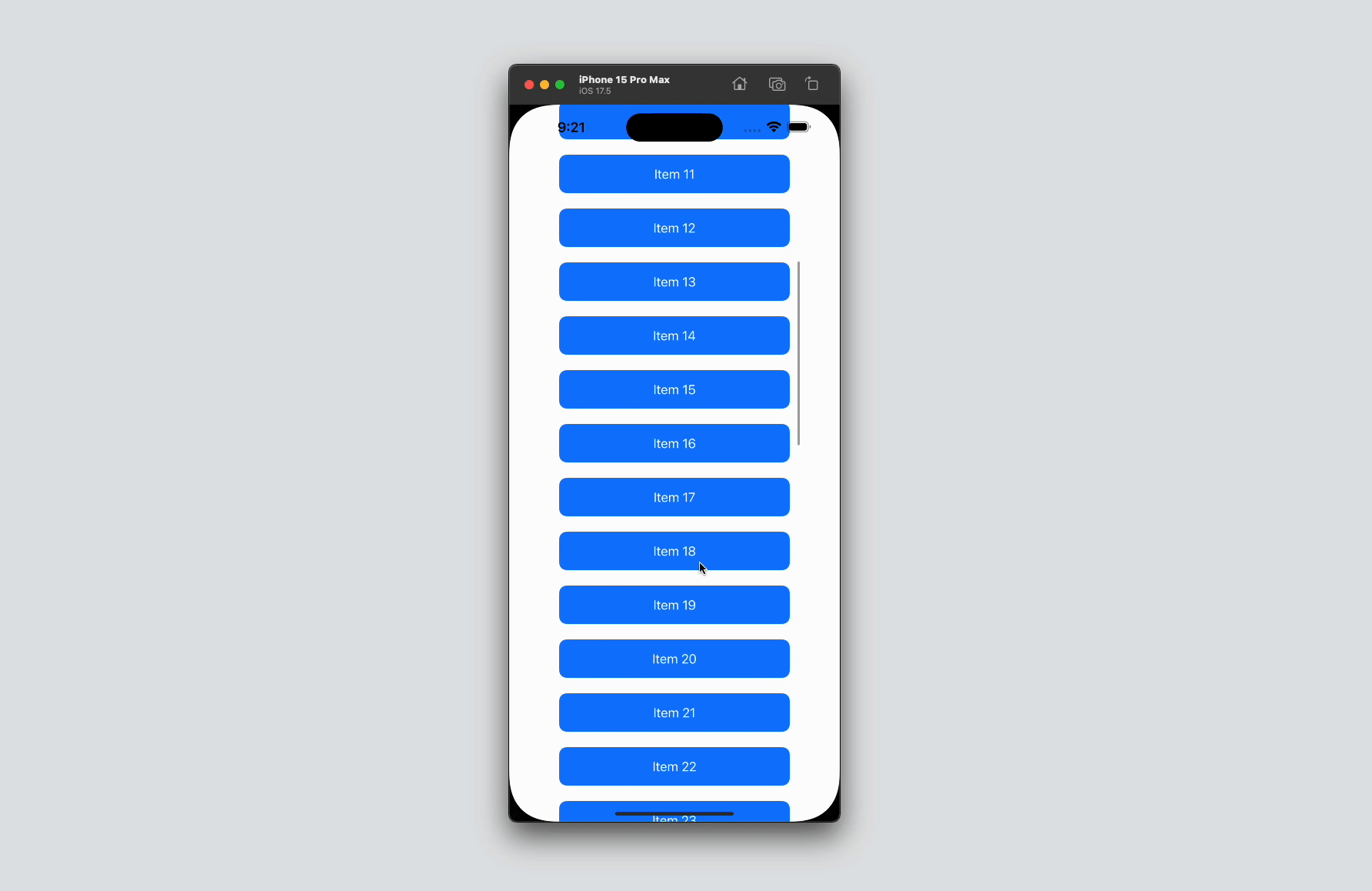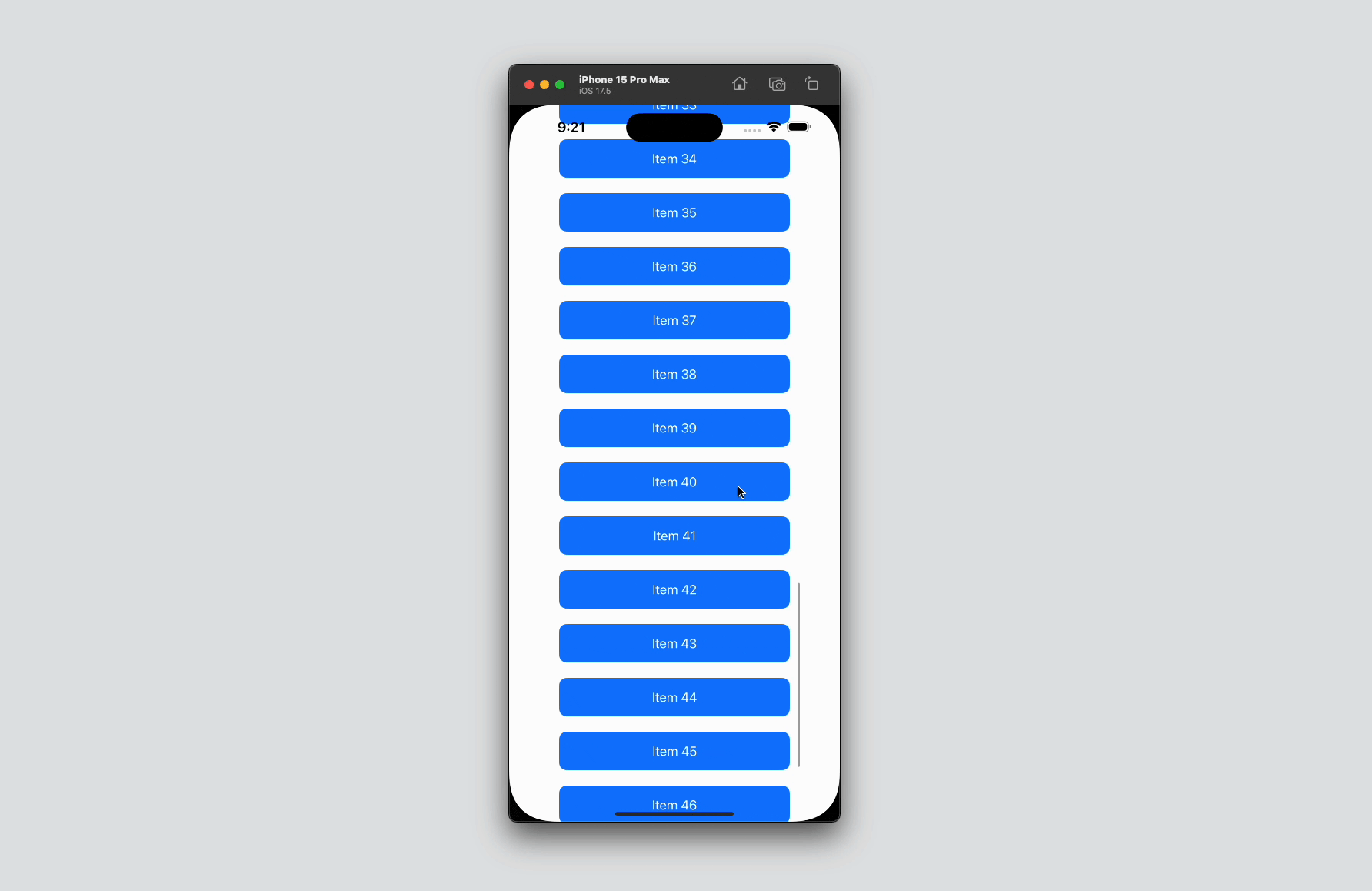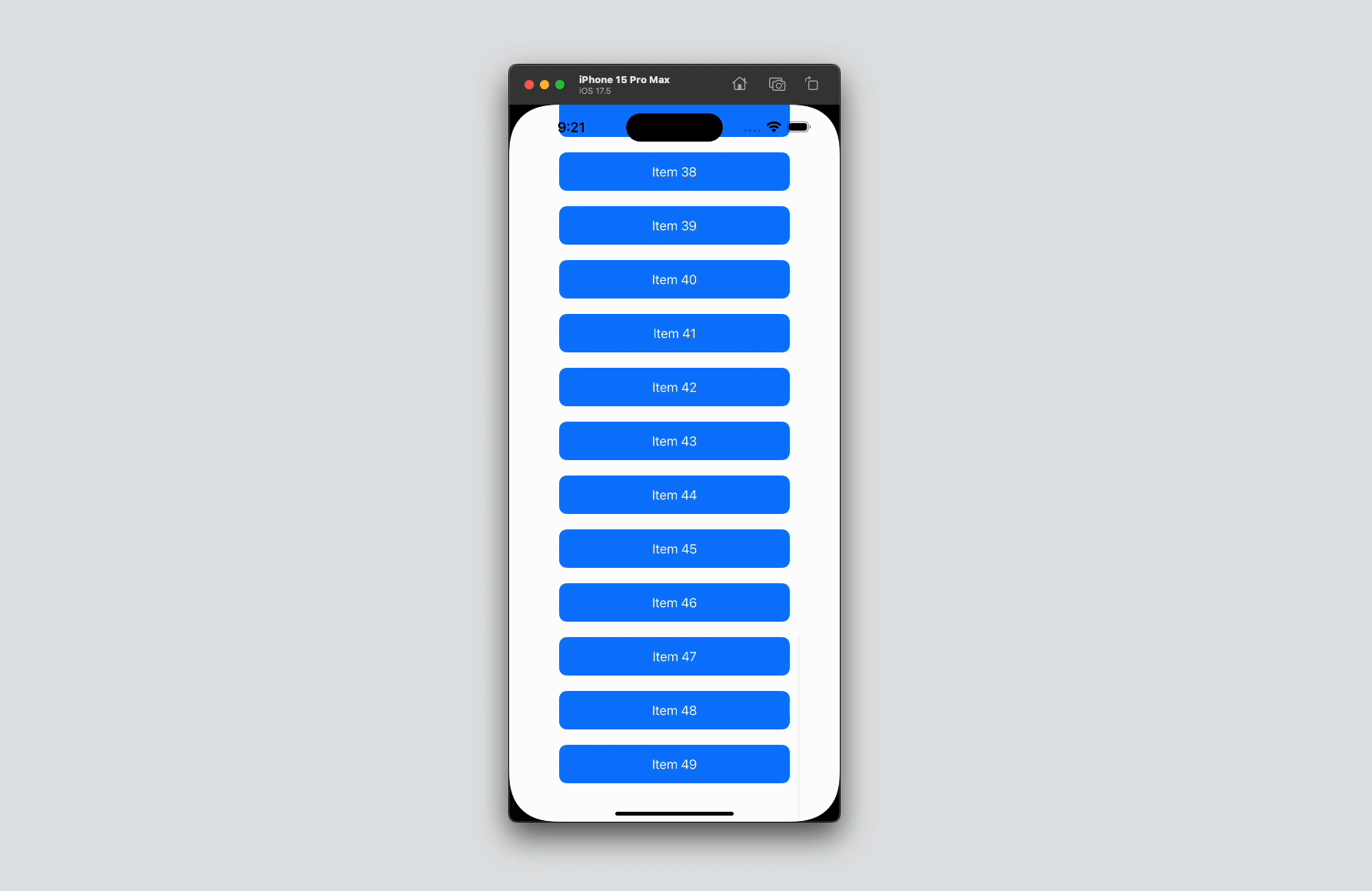
Code Snippet
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
ScrollView {
VStack(spacing: 20) {
ForEach(0..<50) { index in
Text("Item \(index)")
.frame(width: 300, height: 50)
.background(Color.blue)
.foregroundStyle(.white)
.clipShape(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10))
}
}
.padding()
}
}
}Code Explanation
ScrollView: This is the main container that provides scrollable content. By default,ScrollViewscrolls vertically.VStack(spacing: 20): TheVStackarranges its children in a vertical line, with a spacing of 20 points between each item.ForEach(0..<50) { index in ... }: This loop creates 50 items, each represented by aTextview displaying the item number.Text("Item \(index)"): Each item is a text view showing the index number..frame(width: 300, height: 50): Sets the width and height for each item..background(Color.blue): Sets the background color of each item to blue..foregroundStyle(.white): Sets the text color to white..clipShape(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10)): Rounds the corners of each item..padding(): Adds padding around theVStack.
Customizing ScrollView
- Horizontal ScrollView: To make the scroll view scroll horizontally, you can specify the
axesparameter.

ScrollView(.horizontal) {
HStack(spacing: 20) {
ForEach(0..<50) { index in
Text("Item \(index)")
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
.background(Color.green)
.foregroundStyle(.white)
.clipShape(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10))
}
}
}- Vertical and Horizontal ScrollView: To support both vertical and horizontal scrolling, use
.verticaland.horizontaltogether.

ScrollView([.horizontal, .vertical]) {
VStack(spacing: 20) {
ForEach(0..<50) { index in
Text("Item \(index)")
.frame(width: 100, height: 100)
.background(Color.red)
.foregroundStyle(.white)
.clipShape(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10))
}
}
}- ScrollViewReader: Allows programmatic scrolling to specific views.
ScrollView {
ScrollViewReader { proxy in
VStack(spacing: 20) {
ForEach(0..<50) { index in
Text("Item \(index)")
.id(index)
.frame(width: 300, height: 50)
.background(Color.blue)
.foregroundStyle(.white)
.clipShape(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10))
}
Button("Scroll to Item 25") {
proxy.scrollTo(25, anchor: .center)
}
}
.padding()
}
}Visibility of the Scroll bar Indicator
ScrollView (.vertical, showsIndicators: false) {
VStack {
ForEach(0..<20) { index in
Text("Item \(index)")
.id(index)
.frame(width: 300, height: 50)
.background(Color.blue)
.foregroundStyle(.white)
.clipShape(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10))
}
}
}The showsIndicators parameter in line 1 takes in true or false to show or hide the scroll bar indicator respectively. The default setting is true.
Scroll views in SwiftUI provide a flexible and efficient way to display content that exceeds the visible screen area. By using the ScrollView component, developers can easily create scrollable interfaces that enhance the user experience. Customizations such as horizontal scrolling, combined scrolling, and programmatic scrolling with ScrollViewReader offer powerful tools to meet diverse UI requirements.




